
cookware kitchenware pot and pan



CHANGWEN COOKWARE ADVANTAGE
We cater for your every single need for stainless steel cookware.

Production Service
We provide ONE-STOP SERVICE for worldwide importers, distributors and retail chains with all parts included

Personalized customization scheme
Independent production of accessories, autonomous pattern designs, self-developed molds, and an in-house printing center for packagings can make your ideas come true
Cost-Effectiveness
Our production strictly follows internationally recognized quality control systems and testing requirements, which will make every penny well spent.

Delivery Time Guarantee
The raw material, components, molds during the entire progress are processed and produced by ourselves without being affected by suppliers, which enables us to control the lead time more easily.
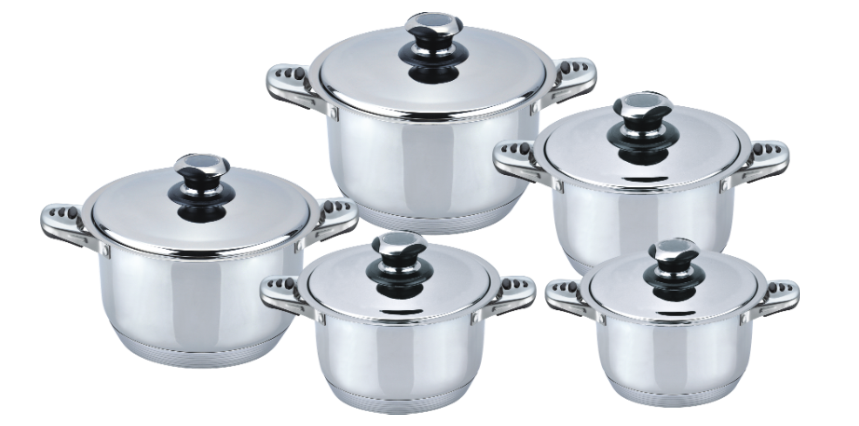
PRODUCT CATEGORIES
Premium stainless steel material with timeless design & high performance.
Cookware set, stock pot, saucepan, frying pan, work, Steamer, …
About
CHANGWEN Manufacturer

A famous stainless steel production base in China since 2002
20-year professional manufacturing experience in stainless steel cookware sets, cutlery and whistling kettles
Customized ONE-STOP SERVICE
97,910-square-meter factory with automated production lines
Internationally recognized certificates from BSCI, FDA, LFGB, etc.
Export to countries and regions around the world
Punctual delivery




HOT SALES PRODUCTS
We manufacture nearly all types of cookware products you can think of: Saucepans, casseroles, fry pans, skillets, woks, roasters, kettles, smokers, steamers, chef’s pans, teppanyaki plates, stockpots, etc.

CUSTOMER-ORIENTED SOLUTION
Our customization service aiming at customers’ sore points enables ideas and proposals to be realized within 25 days in our sample center, giving credit to independently produced components, and to self-designed and self-developed molds.
Learn More About Our Offering >CONTACT US
Want to hit your market with the most stylish & cost-effective cookware ? Contact your specialized manufacturer today!
Contact Us >E-mail: changwen@cwcooking.com
Phone: 0086-13929001235

 English
English Español
Español



















